
About your knee pain and treatment options.
A healthy knee joint can move easily. But when you have arthritis, the pain can severely limit your ability to move and to enjoy life. Explore your treatment options and see if you’re a candidate for knee replacement surgery using ARVIS®.
How your knee works.
The knee is the body’s largest weight-bearing joint. Three bones meet to form your knee joint – your thighbone, shinbone, and kneecap. A layer of cartilage tissue covers the end of the thighbone and the top of the shinbone. A healthy knee and healthy cartilage absorb stress and allow the femur to glide on the shinbone.

Common causes of knee pain.
Arthritis is a condition that affects the cartilage of the joints and is the primary cause of knee pain. As the cartilage lining wears away, the protective lining between the bones is lost. As a result, painful bone-on-bone arthritis develops, which can restrict motion in your knee and reduce your quality of life. Other factors that contribute to knee pain include age, genetics, excessive weight, and injury.
What are the treatment options?
Depending on your diagnosis and the severity of your knee arthritis, your treatment options may include:
Medication
Joint fluid supplements
Physical Therapy
Injections
Weight Loss
(If appropriate)
Knee replacement surgery
Knee replacement surgery.
If conservative treatments have not been effective for your knee pain, talk to your doctor about a knee replacement using ARVIS augmented reality. It’s time to consider surgery when arthritis limits your everyday activities like walking, bending your knees, and sleeping and when you get little pain relief from anti-inflammatory drugs or other treatments such as physical therapy.
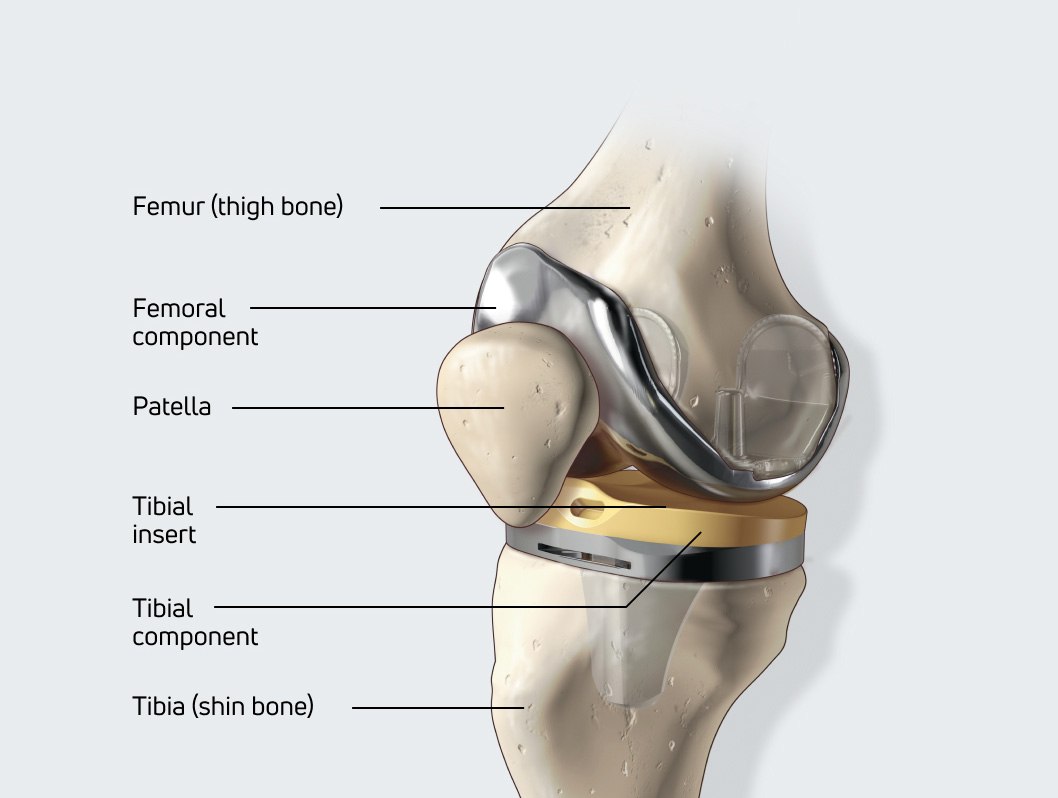
Knee replacement involves the removal of arthritic bone ends and damaged cartilage and replacing them with prosthetic implants that replicate the knee joint.
Knee replacement surgery with ARVIS.®
Before surgery, ARVIS attaches to your surgeon’s surgical helmet or headband. Once your surgeon gains exposure to the joint, they will attach trackers to your knee. ARVIS uses infrared cameras to locate the trackers thereby letting the computer know where you knee is in space. Your surgeon will see an overlay of real-time navigation information on the operating room table allowing him or her to set the instrument guides in the optimal position for your unique knee.
How it works
Step 1
The damaged portion of tissue on the end of the thighbone is removed and resurfaced into a shape that matches the inside surface of the new metal femoral component
Step 2
The femoral component is then placed on the end of the thighbone. The damaged portion of tissue on the shinbone is removed, resurfaced, and resized to fit the new metal tibial component.
Step 3
The metal tibial component is inserted into the bone, and a polyethylene (plastic) insert is snapped into place.
Step 4
The femoral component will slide on the plastic tibial component as you bend your knee. In most cases, the kneecap is also replaced with a medical-grade plastic component.
Step 5
Your surgeon will conduct several tests during the surgery to help ensure you regain good balance and motion in your knee.